

In an ionic bond, the atoms are bound by attraction of opposite ions, whereas, in a covalent bond, atoms are bound by sharing electrons. In ionic lattices the coordination number refers to the number of connected ions. When all the ions are approximately the same size, they can form a different structure called a face-centered cubic (where the weight is 4 * atomic weight), but, when the ions are different sizes, the structure is often body-centered cubic (2 times the weight). This unit cell has a weight that is the same as 1 of the atoms involved. This is as if all the atoms were placed at the corners of a cube. The simplest form of ionic crystal is a simple cubic. Ionic compounds in the solid state form a continuous ionic lattice structure in an ionic crystal. However, 2+ ions (Be 2+) or even 1+ (Li +) show some polarizing power because their sizes are so small (e.g., LiI is ionic but has some covalent bonding present). Larger negative ions are more easily polarized, but the effect is usually only important when positive ions with charges of 3+ (e.g., Al 3+) are involved (e.g., pure AlCl 3 is a covalent molecule). This polarization of the negative ion leads to a build-up of extra charge density between the two nuclei, i.e., to partial covalency. Ions in crystal lattices of purely ionic compounds are spherical however, if the positive ion is small and/or highly charged, it will distort the electron cloud of the negative ion. They generally have a high melting point and tend to be soluble in water. Ionic compounds conduct electricity when molten or in solution. The larger the difference in electronegativity between two atoms, the more ionic the bond. All ionic bonds have a degree of covalent bonding or metallic bonding. Pure ionic bonding is not known to exist. The low electronegativity of metals and high electronegativity of non-metals means that the energy change of the reaction is most favorable when metals lose electrons and non-metals gain electrons. The larger the resulting energy change the stronger the bond.
POLYATOMIC ION BONDING FREE
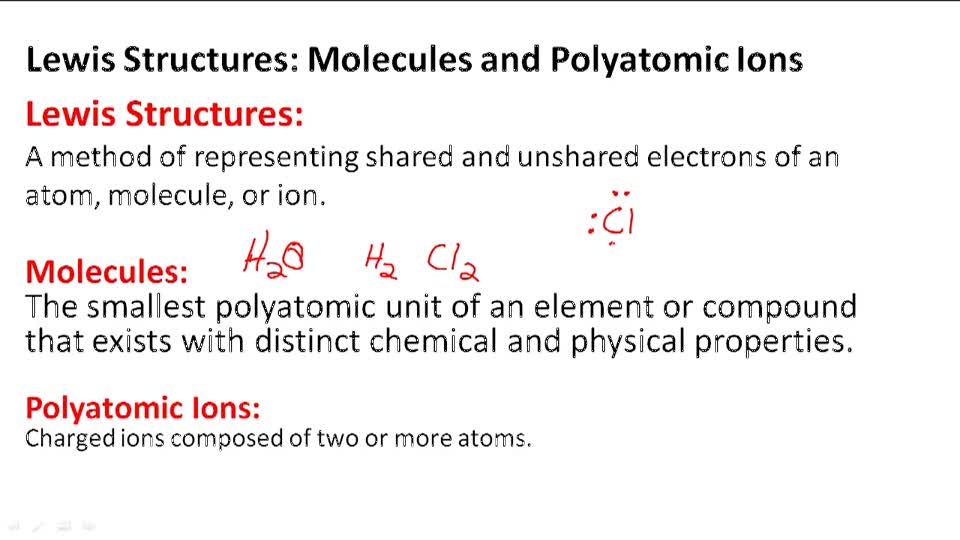
Ionic bonding will occur only if the overall energy change for the reaction is favourable – when the bonded atoms have a lower energy than the free ones. However, the attraction of the ions to each other lowers their energy. There may also be energy changes associated with breaking of existing bonds or the addition of more than one electron to form anions. The removal of electrons from the atoms is endothermic and causes the ions to have a higher energy. These ions are then attracted to each other in a 1:1 ratio to form sodium chloride (NaCl). When sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl 2) are combined, the sodium atoms each lose an electron, forming a cation (Na +), and the chlorine atoms each gain an electron to form an anion (Cl -). The electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions causes them to come together and form a bond.įor example, common table salt is sodium chloride. These electrons then enter the non metal, causing it to form a negatively charged ion or anion which also has a stable electron configuration. The metal donates one or more electrons, forming a positively charged ion or cation with a stable electron configuration. An ionic bond (or electrovalent bond) is a type of chemical bond that can often form between metal and non-metal ions (or polyatomic ions such as ammonium) through electrostatic attraction.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
